At some point, almost everyone has asked themselves, “What is my BMI?” The question comes up at doctor’s visits, during fitness programs, or even casually when browsing health articles. For many, the number on the scale feels like the ultimate measure of health, but weight alone doesn’t tell the whole story. Two people may weigh the same, yet their health profiles could be completely different depending on how their weight is distributed between muscle and fat.
BMI can be useful in this situation. By comparing weight with height, it offers a brief overview that puts weight into perspective. BMI provides a standardized method of screening for underweight, healthy weight, overweight, or obesity rather than depending on guesswork. A BMI calculator is a straightforward, universal point of reference that anyone can use, but it cannot take the place of a comprehensive medical evaluation.
Knowing your BMI is a first step toward greater health awareness, regardless of whether you’re tracking fitness objectives or are simply inquisitive.
Table of Contents
- Understanding BMI: The Basics
- Men vs. Women: How BMI Differs
- The Role of Age in BMI Calculations
- How to Calculate BMI: Manual vs. Online
- Interpreting Results Across Life Stages
- Limitations of BMI and Why It Still Helps
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Understanding BMI: The Basics
BMI stands for Body Mass Index, and it’s a formula that compares a person’s weight to their height. The idea is straightforward: divide your weight in kilograms by your height in meters squared. If you’re using pounds and inches, the formula is slightly adjusted, but the principle is the same.
Example: Suppose someone weighs 70 kilograms and is 1.75 meters tall. First, square the height: 1.75 × 1.75 = 3.06. Next, divide the weight by this number: 70 ÷ 3.06 = 22.9. That person’s BMI is 22.9.
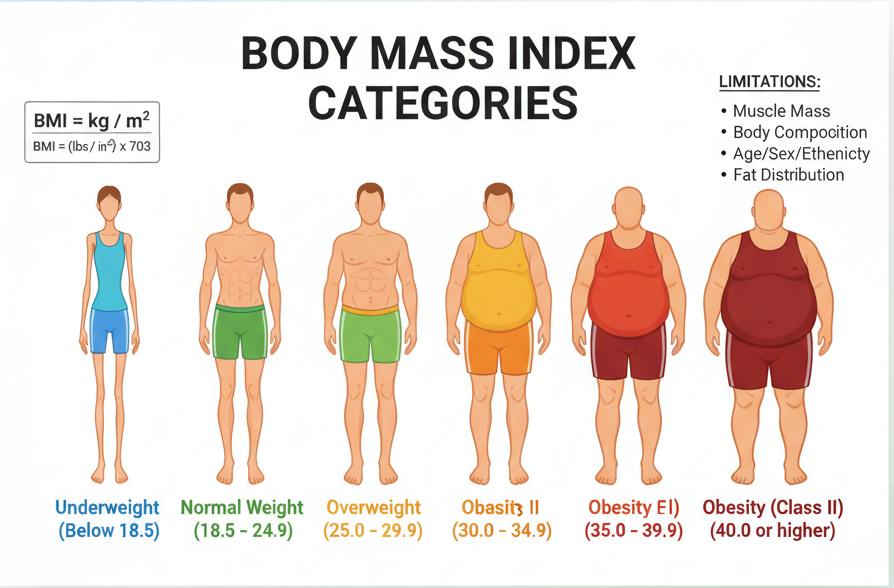
The BMI scale helps interpret this number. A BMI below 18.5 is considered underweight, between 18.5 and 24.9 is a healthy range, 25 to 29.9 is overweight, and 30 or above is classified as obese. While these categories are general, they provide a helpful framework for understanding where you stand. That’s why a body mass index calculator or BMI calculator online can be so beneficial, as they do the math for you in seconds.
Men vs. Women: How BMI Differs
Although BMI uses the same formula for everyone, the way results are interpreted can differ between men and women. This is because men typically have more muscle mass, while women naturally carry more essential body fat for hormonal and reproductive health. For example, a BMI of 25 might look very different on a man with broad shoulders and more muscle compared to a woman with the same BMI but different body composition.
This is why tools like a BMI calculator for men or a BMI calculator for women can help you get tailored insights. They might provide explanations that take these biological variations into account, but they don’t alter the formula itself. It’s critical to keep in mind that BMI is a recommendation rather than a final judgment. Similar to how a woman with a “normal” BMI may still have higher body fat that compromises her health, an athletic man with a high BMI because of muscle may still be in excellent health.
The Role of Age in BMI Calculations
Another key factor in BMI interpretation is age. For children and teens, BMI is not read on the standard adult scale but compared to growth charts and percentiles. A 12-year-old boy with a BMI of 20, for example, may fall into a healthy range for his age and development, even though that same number could mean something else for an adult. This is where a BMI calculator with age becomes important, as it adjusts results according to age-specific benchmarks.
For adults, the categories remain fixed: underweight, healthy, overweight, and obese. However, as people grow older, the interpretation can shift slightly. Research shows that older adults may benefit from carrying a bit more weight, as being slightly above the “healthy” range may actually offer protection against frailty or bone density loss.
How to Calculate BMI: Manual vs. Online
Calculating BMI manually isn’t tricky, but it does involve some math. Take your weight in kilograms and divide it by your height in meters squared. For example, if you weigh 80 kg and are 1.8 meters tall, first square your height (1.8 × 1.8 = 3.24). Then divide 80 ÷ 3.24 = 24.7. Your BMI would be 24.7, which falls at the higher end of the healthy range.
That said, most people prefer to skip the math and use a body mass index calculator. An online BMI calculator can instantly generate your result once you enter your height and weight. Many tools also allow you to switch between units. If you’re used to metric, a BMI calculator in kg works perfectly, while others provide options for pounds and inches.
Interpreting Results Across Life Stages
Once you’ve calculated your BMI, the next step is understanding what the number really means. A BMI below 18.5 is considered underweight, which can signal risks such as poor nutrition, low immunity, or bone weakness. A “normal” BMI, between 18.5 and 24.9, is generally associated with minimal risks of chronic disease and better overall health outcomes.
Moving into the 25 to 29.9 range is categorized as overweight, which can raise the chances high blood pressure or diabetes if not managed carefully. A BMI of 30 or higher drops into the obese category, where risks for heart disease, metabolic disorders, and joint strain become more pronounced.
But these categories don’t apply equally to everyone. A 20-year-old athlete with a BMI of 27 may simply have more lean muscle, while an older adult at the same BMI may be carrying excess fat. The situation is also altered by gender; men typically have more muscle, but women naturally need more essential body fat. Because of this, utilizing tools such as a BMI calculator for women, a BMI calculator for men, or even a BMI calculator that accounts for age can improve the accuracy of interpretation.
Limitations of BMI and Why It Still Helps
BMI is a simple calculation, but it comes with limitations. It doesn’t measure body fat directly, nor does it distinguish between fat, muscle, or bone density. This can lead to misclassifications. For example, a professional athlete might fall into the overweight range because of high muscle mass, not excess fat. On the other hand, an elderly person with low muscle mass might show a “normal” BMI even though they have higher fat levels.
Despite these flaws, BMI remains one of the most widely used screening tools worldwide. Its strength lies in its simplicity; it requires only height and weight, yet it can flag potential risks that warrant further investigation. In other words, a body mass index calculator or BMI calculator online is not a final verdict on health, but a useful first step in identifying where more attention might be needed.
Conclusion
BMI may not be perfect, but its simplicity makes it an important starting point. Instead of guessing, you can quickly answer the question, “What is my BMI?” and place your weight in context with your height, age, and gender. Online tools like a BMI calculator in kg/cm, or tailored versions for men and women, make it accessible to anyone.
The key is to use BMI as a guide rather than a judgment. It can spark awareness, encourage healthier habits, and highlight when a deeper medical evaluation may be needed. So the next time you’re curious about your health, try a BMI calculator; it’s a fast way to see where you stand on the scale.
FAQs
How do I calculate my BMI?
Divide your weight in kgs by your height in meters squared, or use a BMI calculator online to do the math instantly.
Do men and women use different BMI calculators?
The formula is the same, but a BMI calculator for men and a woman’s BMI calculator can provide different results, since body composition varies.
Does age change my BMI result?
Yes, children and teens use percentiles, and older adults may have slightly different healthy ranges.
Is BMI accurate for athletes?
Not always. Athletes with high muscle mass can look overweight on the BMI scale, even if their body fat is low.